What Are the Three Types of Point Mutation Describe Each
A single nucleotide mutation in the DNA that results in a different amino acid. It occurs when a base pair is deleted from a sequence.
Explain how errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations.
. Point mutations occur at a single site within the DNA. AAA changes to AAT mutation of third nucleotide UUU changes to UUA ILE changes to LEU Protein Nonsense Mutation. Only in a nitrogen base that ends up changing the meaning of the genetic code minimally.
Transversion and transition mutation are DNA substitution mutation. Missense mutations erroneous sense are those in which occurs a point mutation ie. 2 Missense mutations occur in the genes which code for different amino acid.
One point was earned for describing RNA splicing as the process of cutting introns In part b the maximum of 4 points was earned. Point mutations occur due to substitutions. It is a point mutation that substitutes a DNA base and changes one amino acid in the protein sequence What is nonsense mutation.
A point mutation is when a single base pair is altered. Name the three types of point mutation and describe each. View the full answer.
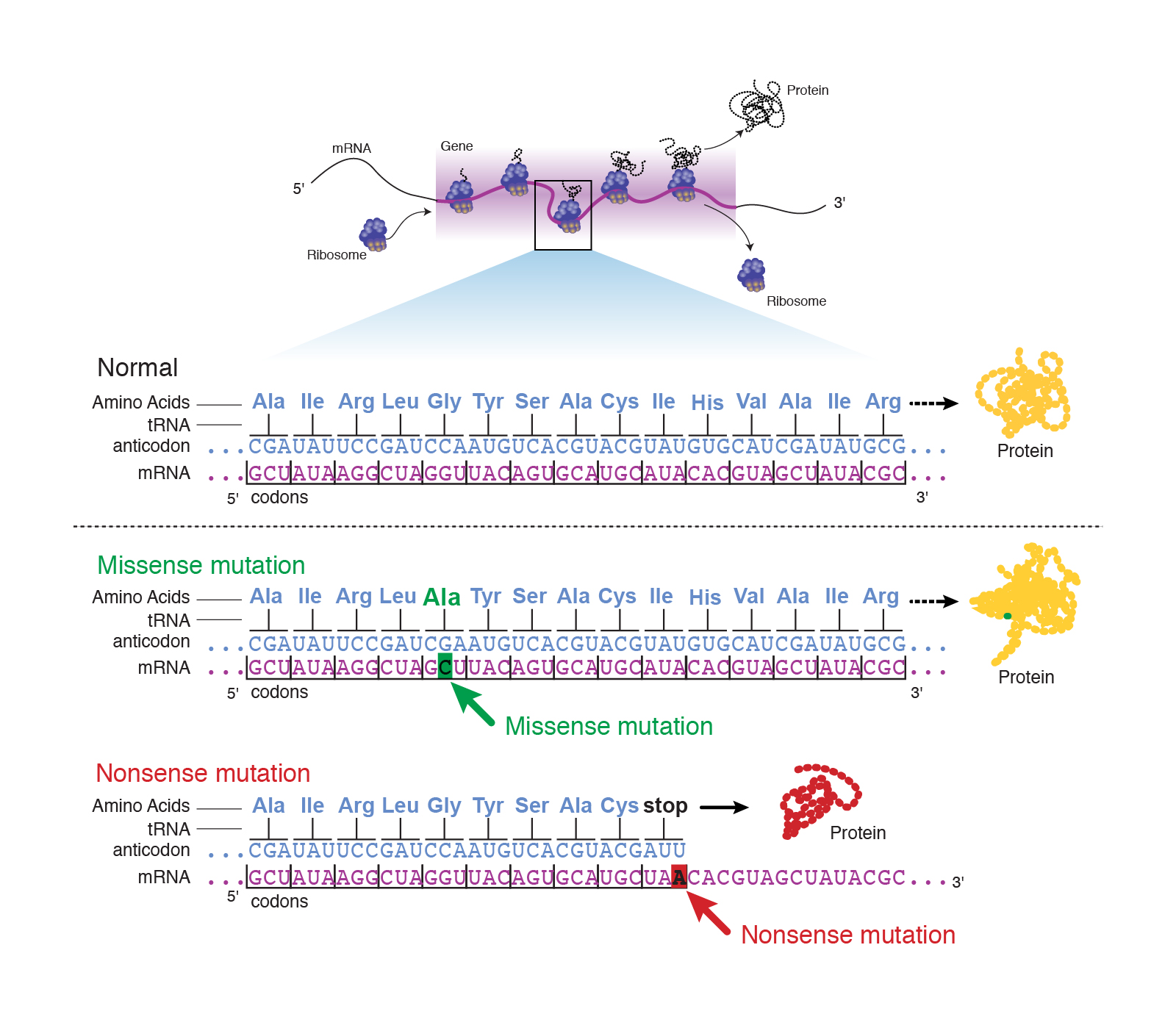
A point mutationthe change of a single nitrogen base in a DNA sequence is usually the least harmful type of DNA mutation. Describe the three different types of point mutation and explain for each what the effect on the final gene product is likely to be. It is further subdivided into three types.
One point was earned for describing a frameshift mutation when a single base is removedlost. Non-sense mutation is one type of point mutation. There are three types of DNA Mutations.
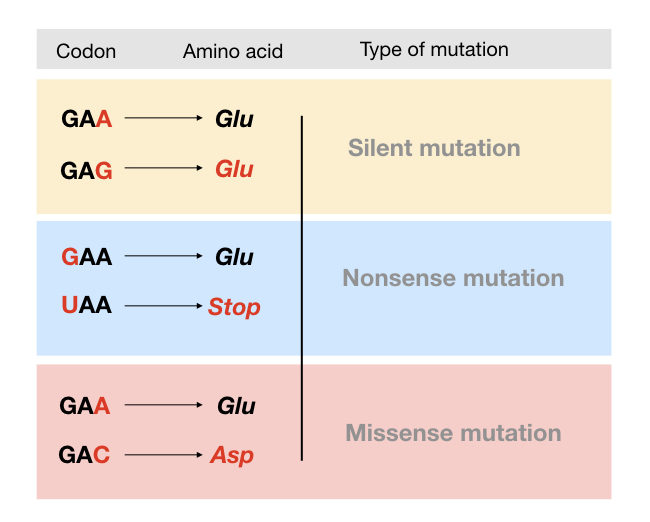
A point mutation that substitutes a DNA base and results in a premature stop codon and results in an incomplete protein that will be non-functional. In the case of silent mutation a nucleotide can be substituted that results in the formation of the same amino acid and this situation can make the multiple codons code for the same amino acid. Base substitutions deletions and insertions.
Point mutation is a single base change in DNA sequence. In part a 1 point was earned for describing how repressor proteins prevent DNA from being transcribed into RNA. Point mutations can be silent missense or nonsense.
Point mutations can have one of three effects. Codons are a sequence of three nitrogen bases in a row that are read by messenger RNA during transcription. An insertion mutation occurs when an extra base pair is added to a sequence of bases.
Insertions are mutations in which extra base pairs are inserted into a new place in the DNA. Deletions duplications insertions inversions and translocations. These two types of point mutations are grouped together because both of them can drastically affect the sequence of amino acids produced.
Frameshift mutations cause alterations of the open reading frame of a protein. Examples of these include silent mutations missense mutations and nonsense mutationsDec 5 2014. List the various types of chemical and physical agents that have mutagenic properties.
First the base substitution can be a silent mutation where the altered codon corresponds to the same amino acid. The three types of point mutations are substitutions insertionsdeletions and mutations. Point mutations can be subdivided into three types.
Second the base substitution can be a missense mutation where the altered codon corresponds to a different amino acid. Since protein-coding DNA is divided into codons three bases long insertions and deletions can alter a gene so that its message is no longer correctly parsed. Instead of substituting one amino acid for another however the altered DNA sequence prematurely signals the cell to stop.
This can occur because of redundancy in the genetic code where an amino acid may be encoded for by multiple codons. In this situation a frame shift occurs and every codon downstream of the mutation is translated incorrectly. 1 Nonsense mutations are the ones which code for the same amino acid.
Deletions are mutations in which a section of DNA is lost or deleted. Frameshift mutations occur due to insertions or deletions of nucleotides. There are 64 codons that code for amino acid out of which three codons UAA UAG UGA are known as termination codons that do not encode for any.
This is when a base pair is added to a sequence - for example AGTCGTAGC could become AGTCG A TAGC. Giving examples summarize the key features of trinucleotide repeat expansion diseases. A deletion mutation is the opposite.
Substitution is where a nucleotide and its corresponding partner nucleotide are replaced with another. Point mutations are the most common type of mutation and there are two types. Give at least one example of each type of agent and describe the types of mutation that they cause.
3 Silent mutations do not affect the function of the proteins and code for different or same amino acid. Single base substitutions are called point mutations recall the point mutation Glu Val which causes sickle-cell disease. Base substitutions deletions and insertions.
The following points highlight the three types of point mutation. This type of mutation is a change in one DNA base pair that results in the substitution of one amino acid for another in the protein made by a gene Figure 1. A nonsense mutation is also a change in one DNA base pair.
It converts GAG sequence into GUG. Point mutation is of three types Subsitution Insertion Deletion B. A change in one or more base sequences in a gene is called point mutation.
What are the three types of point mutation describe each. There are 5 types of chromosomal alterations. DNA is read in small groups of 3 nucleotides each time and each of these combinations codes for a different amino acid except some special combinations.
Single base substitutions are called point mutations recall the point mutation Glu ----- Val which causes sickle-cell disease. That messenger RNA codon is then translated into an amino acid that goes on to make a protein that will be. Silent - A change in the genetic sequence that does not change the protein sequence.
There are three types of DNA Mutations. Now we can classify this mutation as a point mutation since only one DNA base is affected but we can also say that its a nonconservative missense mutation since glutamate is being swapped out for valine and the two are different types of amino acids since glutamate is an acidic amino acid and valine is a nonpolar one. Point mutations are the most common type of mutation and there are two types.

Ls What Is Point Mutation Name A Disease That Is Caused By Point Mutation Ecur 164 Is This A Course About Science Wiki

Difference Between Point Mutation And Frameshift Mutation Definition Types Features Diseases Caused Point Mutation Mutation Biology Notes
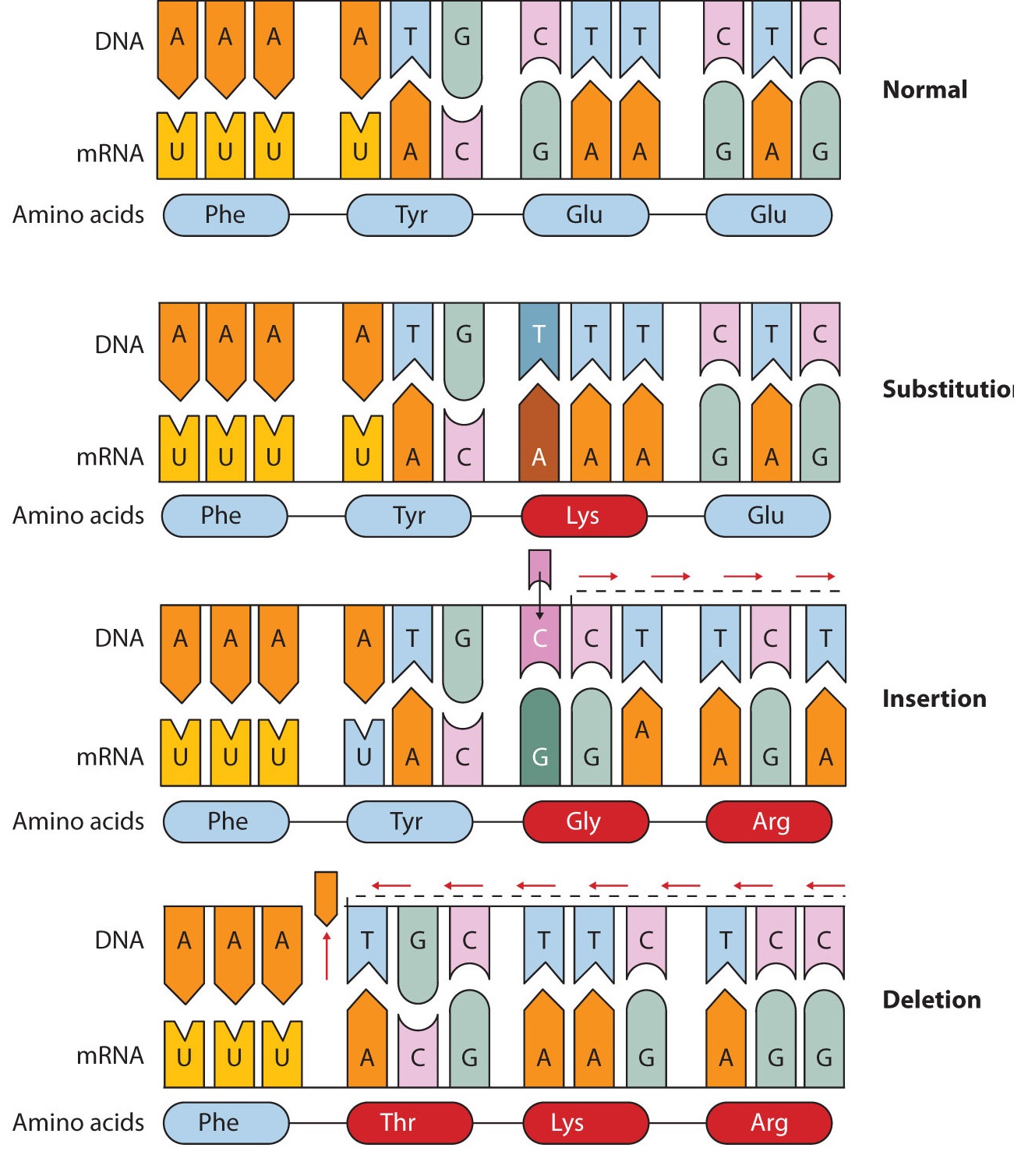
Point Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples Applications
How Does Mutation Affect Dna Replication Socratic

Major Types Of Mutations Biology For Non Majors I
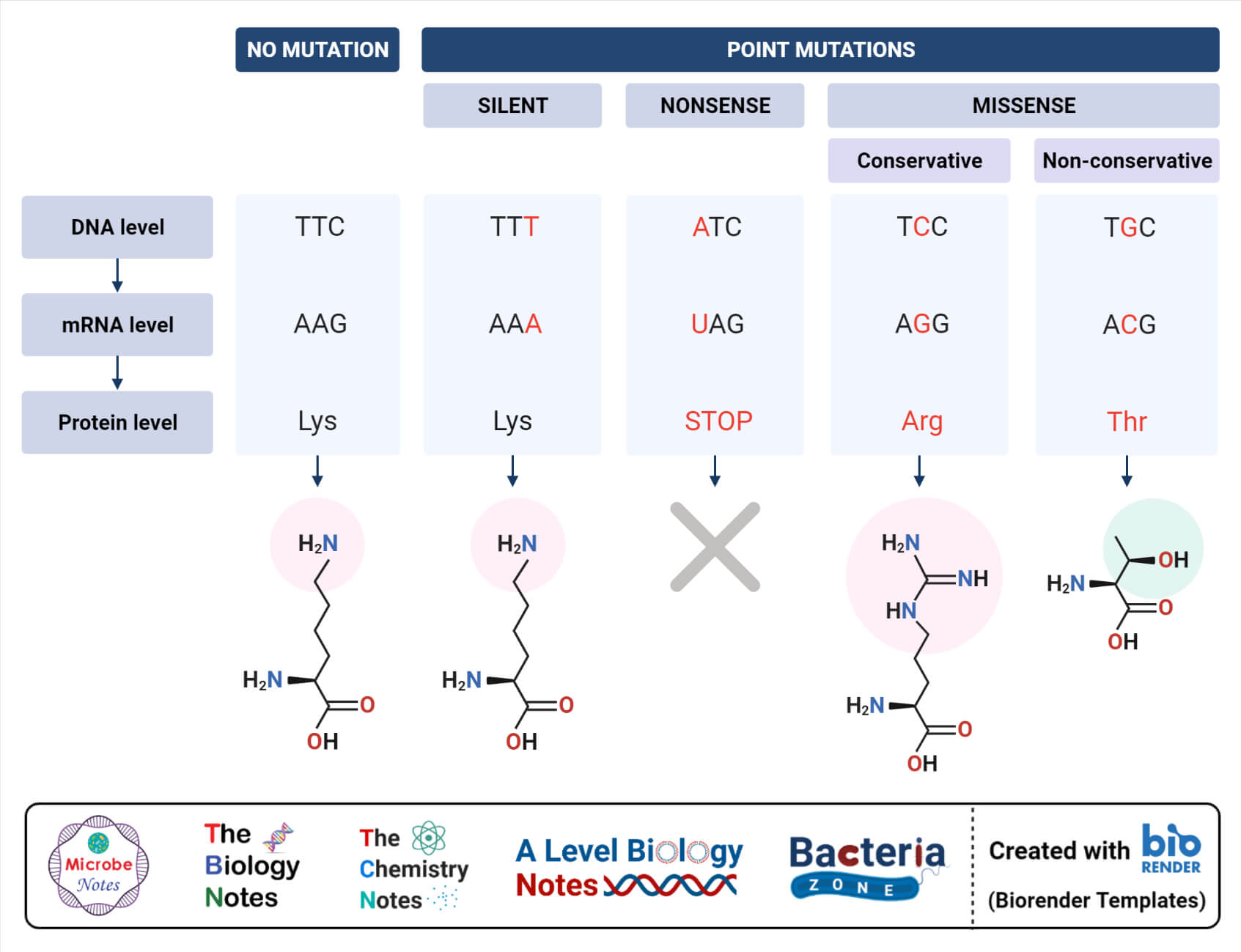
Point Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples Applications
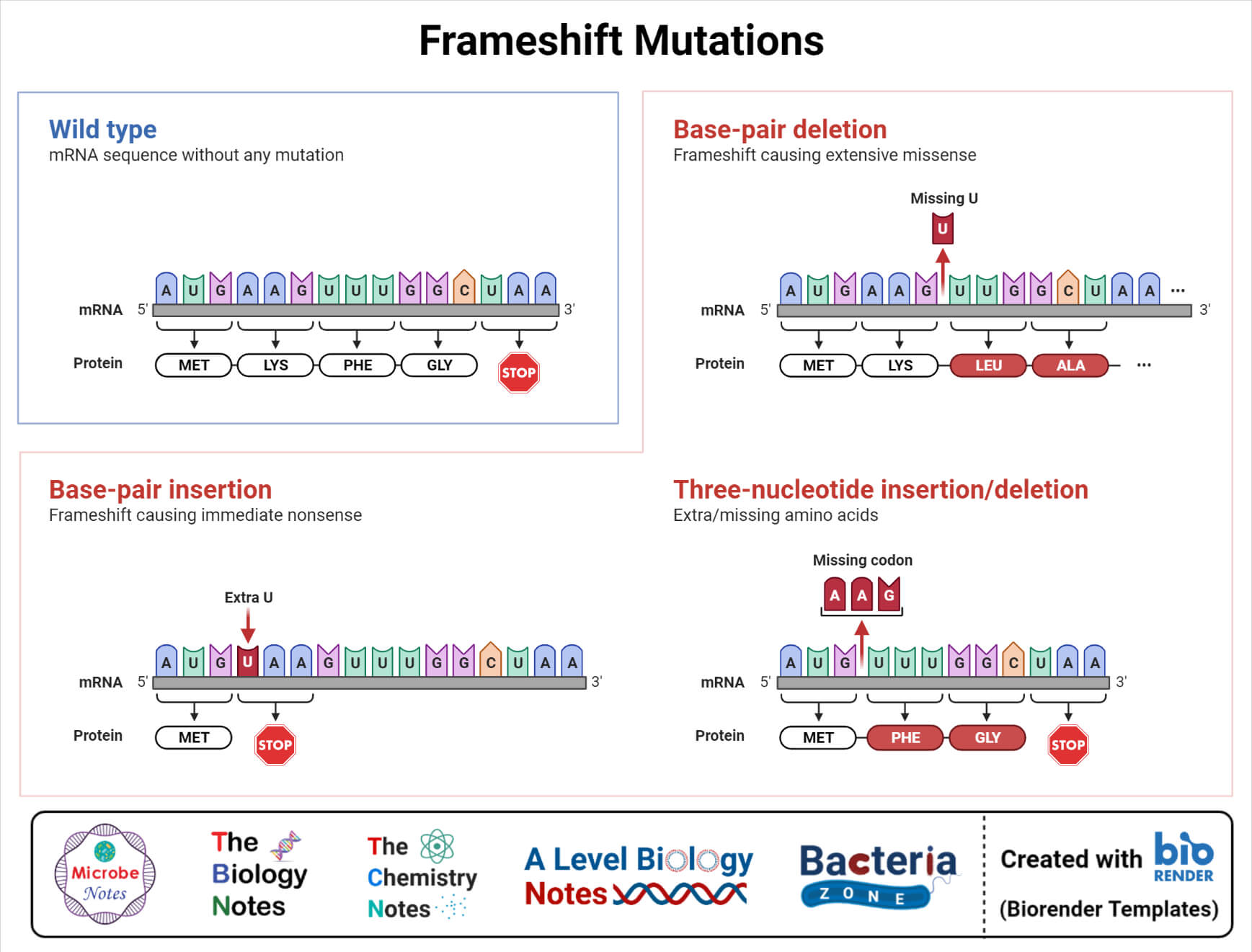
Point Mutation Definition Types Expii
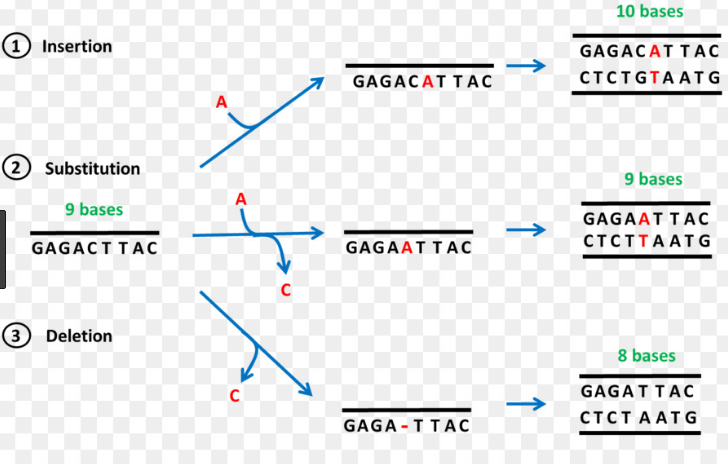
5 Difference Between Frameshift And Point Mutations Viva Differences
Point Mutation Definition Types Examples Biology Dictionary
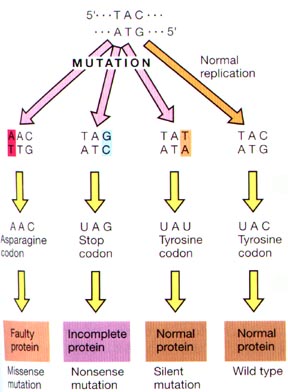
Mutation And Types Of Mutation Online Biology Notes

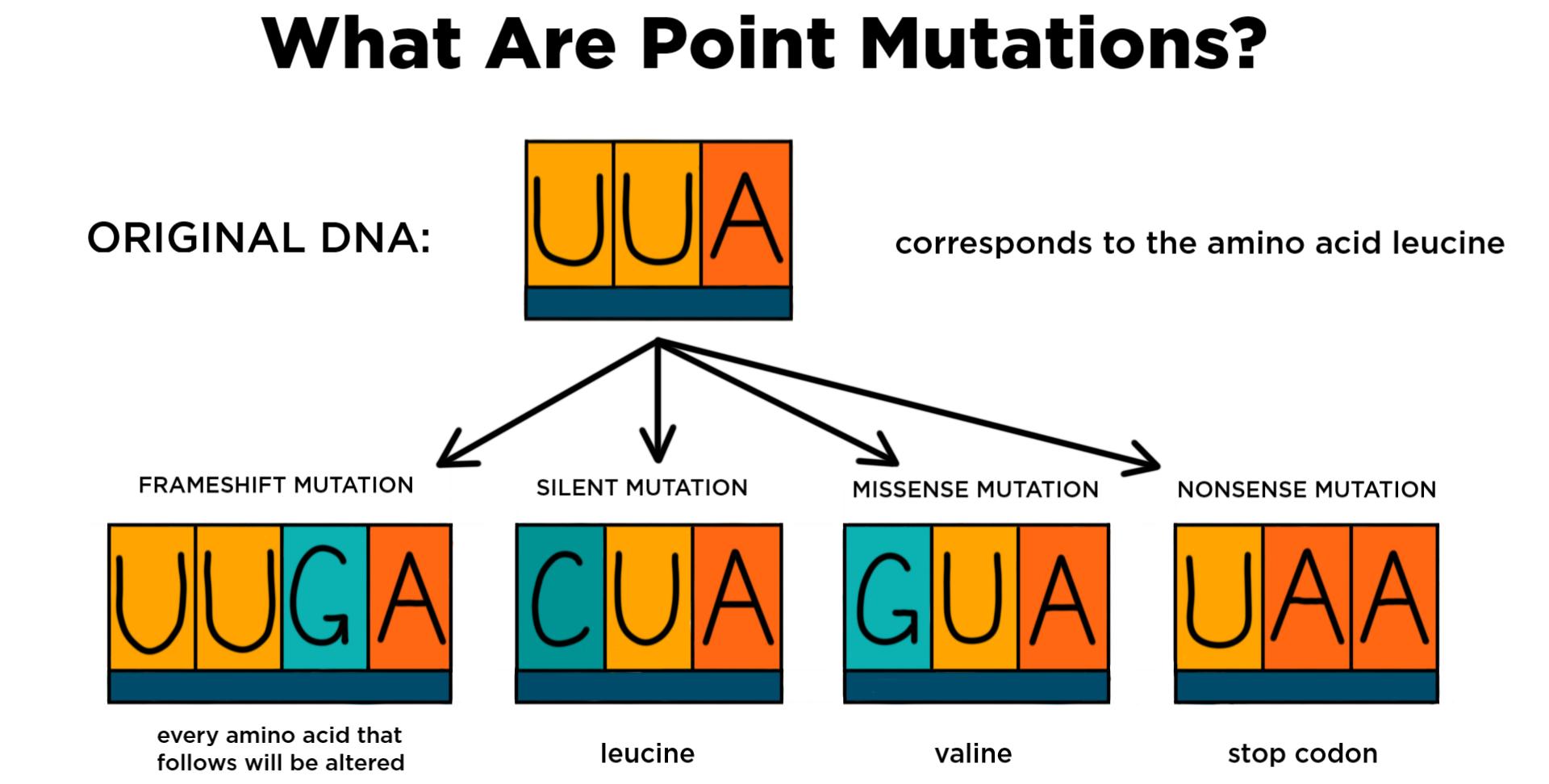
Point Mutation Definition Causes Mechanism Types Examples Applications

19 5 Mutations And Genetic Diseases Chemistry Libretexts

Point Mutations Labster Theory

Silent Mutation Definition Examples Expii
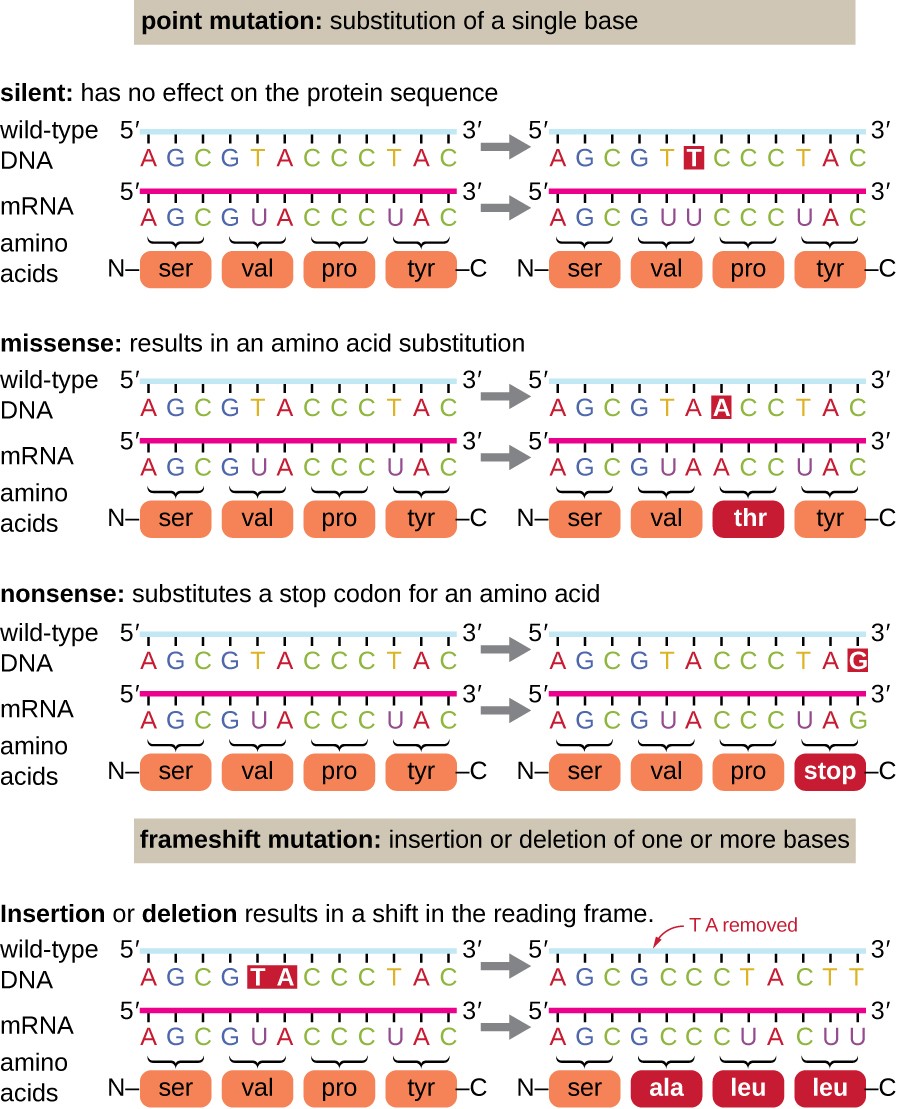
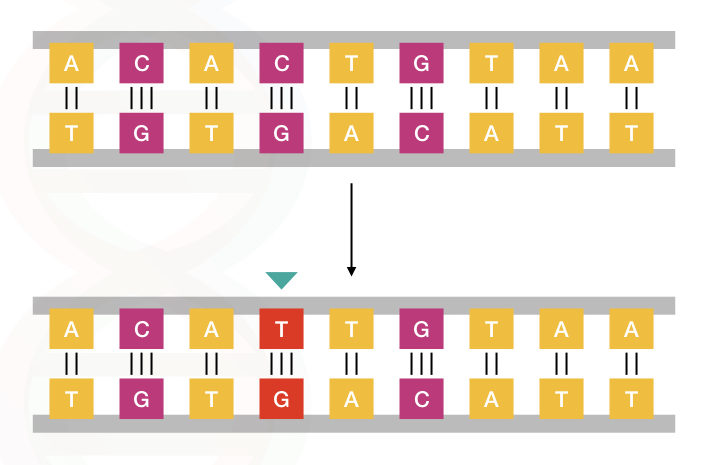


Comments
Post a Comment